
Zoeken:
Winkelwagen:
Categorie:
- Electronica »
- Bouwkits »
- Arduino »
- Arduino shields »
-
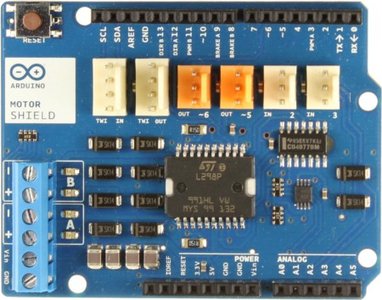
Arduino motor shield, Rev3 A000079
- (Artikelnr: 8079079)
€ 29,95
Prijs per stuk
Aantal:
Bestellen
De Arduino Motor Shield is gebaseerd op de L298, een dual full bridge driver, ontworpen om inductieve belastingen te sturen zoals relais, solenoides, DC en stappen motoren. Het laat toe om 2 DC motoren aan te drijven aan hand van je Arduino bord, de snelheid en richting te bepalen van elke motor afzonderlijk.
Heeft u een vraag over dit product?
Stel ons uw vraag
Stel een vraag over dit product

Jouw vraag is verzonden! Bedankt.
We zullen jou zo snel mogelijk voorzien van een antwoord.
 Vergroot
Vergroot